What is piezoelectric ceramic?
Piezoelectric ceramics are fine ceramics with piezoelectricity. They are used in various fields in our daily lives, as they can convert electric energy into kinetic energy (such as ultrasound and driving force) or kinetic energy into electric energy. Lead zirconate titanate (PZT), which we also provide, shows high piezoelectric performance.
Direct piezoelectric effect
Pressure is applied to the piezoelectric element to generate strain
Voltage (corresponding to strain) is generated

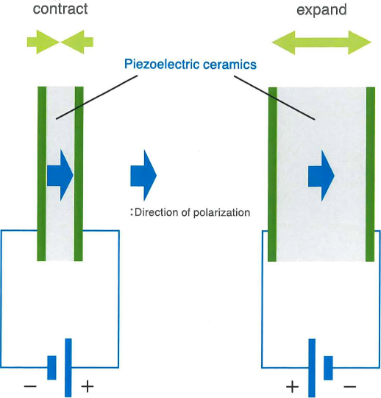
Reverse piezoelectric effect
Voltage is applied to the piezoelectric element
The element generates strain corresponding to the voltage
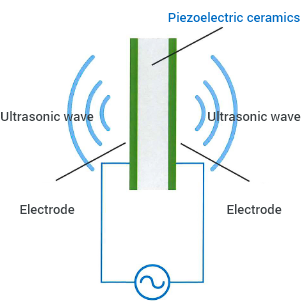
Mechanism of ultrasound generation
By utilizing reverse piezoelectric effect, piezoelectric ceramics extend and shrink (vibrates) depending on the frequency of the voltage that is applied. This vibration generates ultrasound.
What is piezoelectric single crystal?

Compared to ceramic, which is a polycrystalline material with random crystal orientations, a single crystal is a substance in which the crystal orientation only has one direction regardless of its position. Single crystal has superior piezoelectricity compared to conventional piezoelectric ceramics
as the crystal orientation is completely aligned and no grain boundary exist in it.
TFT Corporation provides single crystal products that is composed of lead magnesium niobate-lead titanate (PMN-PT) as their main component. Single crystals are produced by Tayca Corporation (Japan) and TRS technologies, Inc.(The U.S).
Application examples of piezoelectric material
| Function | Application |
|---|---|
|
Electricity Ultrasound Ultrasound Electricity |
Ultrasonic diagnostic devices, endoscopes |
|
Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) |
|
|
Sensors: flowrate, acceleration, space, liquid level, sound pressure |
|
|
Non-destructive Testing devises |
|
|
Filters, oscillators |
|
|
Sonar, fish finders |
|
|
HAPTICS |
|
|
Kinetic energy Electricity |
Sensors: Flow rate, vibration, pressure, shock detection sensors, gyrosensor electronic instruments |
|
Spark plugs, vibration power generation, electronic lighters |
|
|
Electricity Ultrasound |
Ultrasonic cleaning machines |
|
Treatment devices, ultrasonic therapy devices, ultrasonic scalpels, scalers, cutters, atomizers, positioning |
|
|
Electricity Ultrasound Heat |
High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) |
|
Wire bonders (bonding devices for electronic parts) |
|
|
Electricity Kinetic energy |
Endoscopes |
|
Ink jet, fuel injection |
|
|
Artificial muscles (robots), ultrasonic motors (cameras, pumps) |
|
|
Actuators (buzzers, speakers) |
Typical requirements for piezoelectric ceramics and examples of recommended materials
| Needs | Characteristics | Recommended material | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
To increase the vibration |
Coupling Coefficient |
Large |
L-145N |
|
Relative permittivity |
Large |
||
|
Piezoelectric charge |
Large |
||
|
To increease the reception sensitivity |
Coupling Coefficient |
Large |
L-1A |
|
Relative permittivity |
Small |
||
|
Piezoelectric voltage |
Large |
||
|
To use in a high-temperature environment |
Curie Temperature |
Large |
L-1A, H-8 |
|
To drive at a high voltage |
Mechanical Quality Factor |
Large |
H-8 |
|
To suppress the heat generation during operation |
Dielectric Loss Factor |
Small |
H-8 |
|
Mechanical Quality Factor |
Large |
||

